HOW ONLINE LEARNING IS CARRIED OUT IN COMMUNICATION
WHAT IS DATA COMMUNICATION?
Communication is defined as a process in which more than one computer transfers information, instructions to each other and for sharing resources. Or in other words, communication is a process or act in which we can send or receive data. A network of computers is defined as an interconnected collection of autonomous computers. Autonomous means no computer can start, stop or control another computer.
Components of Data Communication
A communication system is made up of the following components:
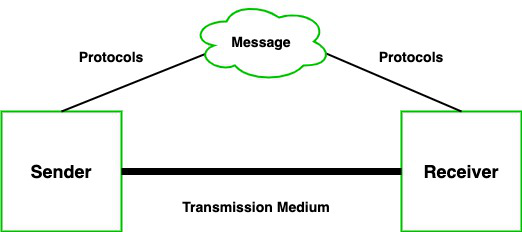
- Message: A message is a piece of information that is to be transmitted from one person to another. It could be a text file, an audio file, a video file, etc.
- Sender: It is simply a device that sends data messages. It can be a computer, mobile, telephone, laptop, video camera, or workstation, etc.
- Receiver: It is a device that receives messages. It can be a computer, telephone mobile, workstation, etc.
- Transmission Medium / Communication Channels: Communication channels are the medium that connect two or more workstations. Workstations can be connected by either wired media or wireless media.
- Set of rules (Protocol): When someone sends the data (The sender), it should be understandable to the receiver also otherwise it is meaningless. For example, Zamani sends a message to Hattan. If Zamani writes in Mandarin and Hattan cannot understand Mandarin, it is a meaningless conversation.
TCP or Transmission Control Protocol is responsible for dividing messages into packets on the source computer and reassembling the received packet at the destination or recipient computer. It also makes sure that the packets have the information about the source of the message data, the destination of the message data, the sequence in which the message data should be re-assembled, and checks if the message has been sent correctly to the specific destination.
IP or Internet Protocol responsible for handling the address of the destination computer so that each packet is sent to its proper destination.
The scenario of this project can be referred to Figure 1. Figure 1 shows the logical network flow from a home network to Cobham College facilities. In this figure, a Cobham College’s student is trying to access the OnlineLearning system located in the Cobham College network facilities. The student is using her modem to connect to the public network before able to connect to the Cobham College facilities. From the Cobham College network, the data then was forwarded to IT Center where the OnlineLearning System server is located.
Based on the scenario given by our esteemed lecturer, Ts. Erman Hamid, we have conducted the 7 Layers OSI model, the subnetting calculation and the TCP/IP setting manual for conducting an online learning for a university. It will includes on how the 7 layers OSI model of communication between student and the university cloud server, the subnetting calculation of each devices from students and university and the TCP and IP Protocol on how to carry out the data.
Here is an example of how the data represented by a file by lecturer to be downloaded by student




Comments
Post a Comment